Scabies disease (Skabies); It is a parasitic disease that progresses with itchy rashes, can be transmitted from person to person, and is more common in public areas during the winter months.
What is the causative agent of the disease?
Scabies, human eye There is Sarcoptes Scabiei, a microscopic arthropod that goes unnoticed. It is a common parasitic disease caused by Hominis.
Who gets the disease?
It can be seen in both genders, all age groups, all ethnic groups, and all socioeconomic levels, without distinguishing between men and women. Because it can cause serious epidemics, it is more common in places where people live, such as nursing homes and dormitories, and in communities with low social levels. It may have a severe course in people with poor body defense mechanisms.
Is the disease contagious?
It usually takes 15-20 minutes from person to person. It can be transmitted even through close contact (such as sleeping in the same bed, holding hands).
What are the symptoms of the disease?
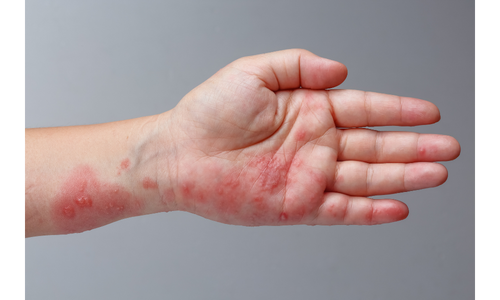
After the parasite is transmitted to the person, it starts to cause complaints after an average of 3-6 weeks. Itching, which increases especially at night and is aggravated by hot baths and showers, is the most important clinical finding. Between the fingers, inside the wrist The body areas where itching and lesions can occur are the face, armpits, behind the ears, waist area, ankles, feet, hips, nipples in women and genital area in men. . The most obvious lesion is the gray-white colored, 1-10 mm long tunnel structures in which the parasite lives, which appear as a wavy dirty line between the fingers. Apart from this, it can cause small bumps and hardness on the skin, blisters and dandruff-scabby lesions.
Where is it seen in children and babies? >
Scalp and face damage occurs in babies and people with low body defense resistance. Involvement can be observed throughout the body, including Although it is rare in adult patients, palmar, sole and facial involvement may occur in infants.
How is it treated?
Treatment depends on the age of the person. It varies depending on the state of the immune system. It should not be forgotten that all family members sharing the same living environment should be treated at the same time, even if they do not have active complaints at that time. Your doctor will recommend treatment for you depending on your age and the status of your complaints. Do not take medication without consulting your doctor. Do not use.
What should be taken into consideration during the treatment?
- Although different drugs can be used in the treatment, which drug should be used? There are some rules that must be followed regardless of whether they are used.
- When local treatment agents are used, care should be taken to apply the medicine to all body parts.
- The laundry and linens used should be at least It needs to be washed at 60 degrees and ironed.
- The items that cannot be washed should be placed in a sealed bag, on average three times. It will be sufficient to keep it for a day.
- After a successful treatment, itching may last for 2-6 weeks.
- It is very important for people who share the same living environment to be treated simultaneously. .


