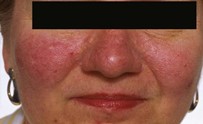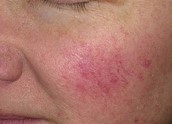
It starts with flushing and burning attacks, especially affecting the middle part of the face, such as the nose, chin, forehead and cheeks, and then acne, permanent redness, increase in capillaries, skin edema and tissue swelling. It is a chronic skin disease that causes skin problems.
Roza disease is also known as rosacea and rosacea.
What are the factors that cause rosacea?
The cause of rosacea is not fully known. Among the factors blamed;
1.Genetic predisposition: Family history. It is present at a rate of 30-40%. However, there is still no clear evidence for genetic transmission.
2. Infectious causes: The most blamed infectious agents are Helicobacter pylori (H pylori) bacteria found in the stomach and demodex mites found on the face.
3.Environmental factors: Ultraviolet light and temperature changes in the environment, wind, exercise, hot baths, alcohol, spicy foods, hot drinks, humidity, cosmetics. Many environmental factors, such as products, play a role in the onset or exacerbation of rosacea lesions.
4.Psychogenic factors: Especially intermittent burning and redness attacks may be affected by changes in the patient's mood and psychological stress.
5.Natural immune system: Recently, an imbalance in the natural defense system of the skin has been mentioned.
What are the clinical features of rosacea and how is it diagnosed?
Mostly between the ages of 30 and 60, with fair skin and colored eyes. It is seen in adults. Although it is more common in women, it is more severe in men.
There are four clinical periods;
1st Period Erythematotelangiectatic: Recurrent burning and redness attacks on the face,
2nd Term Papulopus: Permanent redness in the middle of the face, visible blemishes on the nose and cheeks. Formation of protruding blood vessels,
3rd Term Phymatosis: The redness on the face becomes darker and more permanent, small patches appear on the nose, cheeks, forehead and chin. Formation of red swelling or inflamed pimples (unlike white or blackheads),
4th Period Eyes: Burning or persistent sensitivity in the eyes (eye rosacea) and/or red, swollen nose (rhinophima). p>
The diagnosis is often made according to clinical findings. However, a biopsy may be required to distinguish it from some diseases it is involved in. Specific to rosacea disease There is no laboratory finding.
Is there eye involvement in rosacea?
Approximately 1/3 patients have eye involvement. In 20% of patients, only eye involvement can be observed without skin involvement. Eye involvement is not related to the presence and severity of skin findings.
In eye involvement, findings such as blepharitis, conjunctivitis, keratitis, photophobia, watering, burning, chronic ocular edema, widespread eye pain, and blurred vision can be observed.
What are the factors that increase the clinical symptoms of rosacea?
1.Foods and beverages (hot and cold drinks and foods such as soup, tea-coffee, spicy foods, bitters, pickles, chocolate, alcohol.. .)
2.Weather conditions (sunlight, hot air, cold air, humidity, wind)
3.Psychological stress and excessive exercise
4.Bath, cleaning and personal care products (Hot bath and facial irritating cleaning materials, cologne, tonic, rose water, wet wipes)
5.Medicines (Long-term use of topical corticosteroids on the face)
6.Systemic conditions (premenstrual, pregnancy, menopause, severe cough and constipation)
How is rosacea treated?
Although it is difficult to completely recover from rosacea, it is possible to keep it under control with treatment. General precautions:
The most important thing is to stay away from factors that increase clinical symptoms.
- Using sunscreen:
One of the most important factors that trigger the disease is the sun. Therefore, you should be careful about sun protection throughout your life. You should use a suitable sunscreen recommended by your dermatologist every 2-4 hours a day. You should also wear a sun-protective hat and glasses, wear appropriate clothing and avoid exposure to the sun during peak hours.
- Topical treatment: In mild cases, creams and gels are generally used. The most commonly used are metronidazole (cream, gel, lotion), azelaic acid (cream, gel) and sodium sulfacetamide, sulfacetamide+sulfur. Other drugs are tretinoin, benzoyl peroxide, erythromycin, clindamycin, tetracycline, 5% permethrin cream, tacrolimus and pimecrolimus.
- Systemic Treatment: In severe cases, systemic treatment is applied alone or with topical agents. The most frequently preferred systemic agents are systemic antibiotics (minocycline, doxycycline, tetracycline, metronidazole and azithromycin) and vitamin A product. isotretinoin.
- Laser treatment: Various laser treatments and intense pulsed light (IPL) systems can be effective, especially in the treatment of facial redness and increased capillary vascularization.
- Surgical treatment: Methods such as surgery, cryotherapy, electrocauterization or dermabrasion can be used, especially in severe cases that cause deformities in the nose and cheeks.
Is there a special diet for rosacea?
- Although there is no specific diet for rosacea, you should stay away from foods and drinks that increase facial redness. You should also avoid cigarettes and other tobacco products.
*In our clinic, our patients receive topical creams and systemic medications depending on their disease severity. It can be treated with Max G IPL laser, Nd-Yag laser treatments.