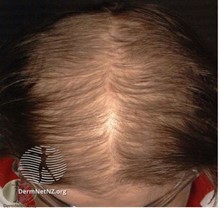
Common progressive disease in genetically predisposed women with a characteristic location distribution. It is defined as thinning and thinning of hair. It is observed frequently.
It is seen in 12% of women around the age of 30 and in 30-40% of women around the age of 60-70. startç As the age decreases, the tendency for clinical severity to increase increases.
What is the cause?
The most common cause is multiple. Although it is thought to be a genetic problem, the problematic genes are currently unknown. Although it is attributed to androgen, which is the second most common cause, its relationship with androgen hormones is not as clear in women as it is in men, so female type hair is the cause. Loss seems to be a more accurate definition. However, it is also observed in people with androgen excess such as excessive hair growth and menstrual irregularities, but in most patients, the serum androgen level in the blood is normal.
When does it start?
Although it can be seen at any age along with menstruation, it is most commonly seen between the ages of 40-50.
How is it observed?
It is usually a slow and progressive hair loss. It starts with the complaint of thinning. It is most commonly seen on the scalp and sides. Unlike men, forehead hair; The line has been preserved. It is classified under various names according to the location and stages of involvement.
How is the diagnosis made?
The diagnosis is made by clinical examination, usually there is no need for biopsy.
How is the diagnosis made?
The diagnosis is made by clinical examination.
p>In clinical evaluation, the distribution pattern, slow onset; shape, family history, hair It is distinguished from chronic telogen shedding by evaluations such as a negative tensile test.
It may also be necessary to check T4, TSH, vitamin D, ferritin levels and androgenic hormone levels.
How is the treatment?
Among the lotions to be applied in the treatment, 2% or 5% minoxidil is a drug with proven effectiveness. It should be used for at least 12 months to evaluate its effect. It should be continued without interruption even after effectiveness is achieved. It should be known that telogen effluvium may be triggered after discontinuation. Additionally, initial shedding may occur within 1-2 months after starting treatment. Unlike men, the effect of the 2.5 mg/day dose of finasteride tablet taken orally has been observed in long-term use. However, due to its significant side effects, it must be used under the supervision of a dermatologist. Results are also obtained with spironolactone, cyproterone acetate, flutamide and cimetidine, whose effectiveness has been proven in some studies. receivable. However, this should be decided by your physician.
Again, hair follicles are used to strengthen the hair follicles on the scalp. The use of mesotherapy and PRP is beneficial.
Recently, successful results have been observed with low-level laser beams, especially in cases thought to be genetically inherited. .