Follic acid hair root. It is inflammation. It can occur anywhere on the body that contains hair. It is seen as a painful swelling surrounding the hair and sometimes as a pus-filled sac located in the middle of it. It often heals spontaneously or with a simple treatment.
It is a common skin disease. It develops when the hair follicle is damaged due to friction or pressure, and microorganisms multiply in that area and cause inflammation. It occurs more easily in folds of the skin, such as the neck and groin, and in areas subject to friction, such as the beard area or genitals.
The causative microorganisms are most often staphylococcus species. Besides bacteria, fungi and viruses can also cause follicitis.
What Facilitates the Development of Follicitis?
Follicitis can develop in anyone. However, it is easier for folliculitis to occur in some cases listed below:
- Heat and sweating
- Obesity
- The skin is tightly covered.
- Shaving (especially close and irritating shaving)
- Tight clothing that causes friction and prevents sweat from evaporating
- Against infectious diseases Presence of some diseases that reduce body resistance (such as diabetes, leucemia, AIDS)
- Presence of a skin disease such as teenage acne or eczema
- Skin integrity ;day&uum; Disabling injuries (abrasions, surgical site incisions, other cuts)
- Long-term use of some medications (corticosteroids and antibiotics)
- Hot bath in an unclean bathtub
- li>
What are the symptoms of folliculitis?
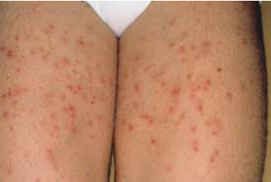
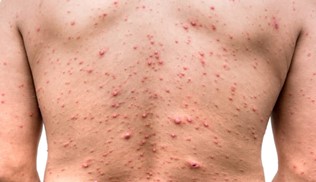
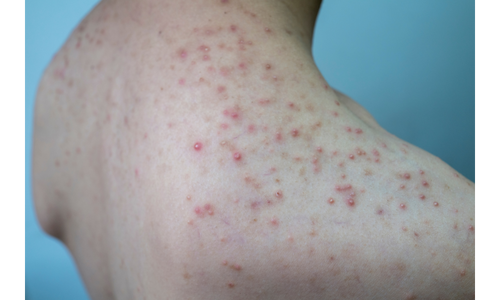
It is seen as a painful red swelling surrounding the hair and sometimes as a pus-filled sac in the middle. It may be accompanied by itching and tenderness. In the following days, crusting may be observed as the purulent swelling opens. Follicitis that progresses deeper than the hair root is called a furuncle. As the inflammation deepens, swelling and tenderness increase. A fewç Inflammation of the hair together is called carbuncle
Can follicitis resolve spontaneously?
Follicitis can occur in a few cases. It heals spontaneously or with a simple treatment within a day. However, in the presence of some risk factors, microorganisms that cause folliculitis may spread to deep tissues and enter the bloodstream. In this case, symptoms such as poor general condition and high fever require urgent treatment. Furuncles and carbuncles, which can be considered as more severe forms of folliculitis (Yavuz Sultan Selim died from carbuncle that was not treated), should always be treated by a physician. Recurrent follicles are hair loss due to damage to the hair follicle. It may cause skin loss and scarring on the skin.
What are the causes of folliculitis?
The microorganisms that most frequently cause folliculitis (living things too small to be seen with the naked eye that can cause infectious diseases, "germs") are bacteria called staphylococci. The virus that causes herpes, pseudomonas bacteria or some other microorganisms and fungi called gram-negative bacteria can also cause folliculitis. Inflammation may develop without a microorganism due to ingrown hair, which is the hair turning back and growing inwards before reaching the skin surface.
How is Follicitis Diagnosed?
Usually, skin examination is sufficient to make a diagnosis. Sometimes your doctor may want to perform an examination called culture antibiogram to understand the causative microorganism and which drugs will be effective. For this purpose, a sample is taken from the contents of the pus-filled sac and examined in the laboratory.
How is Follicitis Treated?
- Situations that facilitate the formation of folliculitis should be eliminated. (such as losing weight, avoiding environments that cause excessive sweating, wearing loose clothes that allow sweat to pass through, not shaving or using an electric razor)
- The skin area with follicles should be gently treated. It should be kept clean with the cleaners applied to it.
- The patient should not squeeze the follicle and try to empty its contents. This is very risky and may cause the microbe to spread throughout the body and cause significant scarring.
- In mild cases, hot compresses and a few warm compresses can be applied to that area. There will be improvement within the day.
- In the treatment of more severe, numerous or advanced folliculitis, the antibiotics your doctor will prescribe will be administered orally and for as long as it is recommended. should be used as follows. In some special cases of folliculitis, your doctor may also prescribe herpes or fungal medications.
- In advanced cases such as furuncles and carbuncles, folliculitis is used to drain the accumulated pus. A minor surgical procedure in the form of an incision may be required.